CIDEA (cell death inducing DFFA like effector a)
- symbol:
- CIDEA
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 18p11.21
- gene_family:
- alias symbol:
- CIDE-A
- alias name:
- None
- entrez id:
- 1149
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000176194
- ucsc gene id:
- uc002kqt.5
- refseq accession:
- NM_001279
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:1976
- approved reserved:
- 1998-07-15
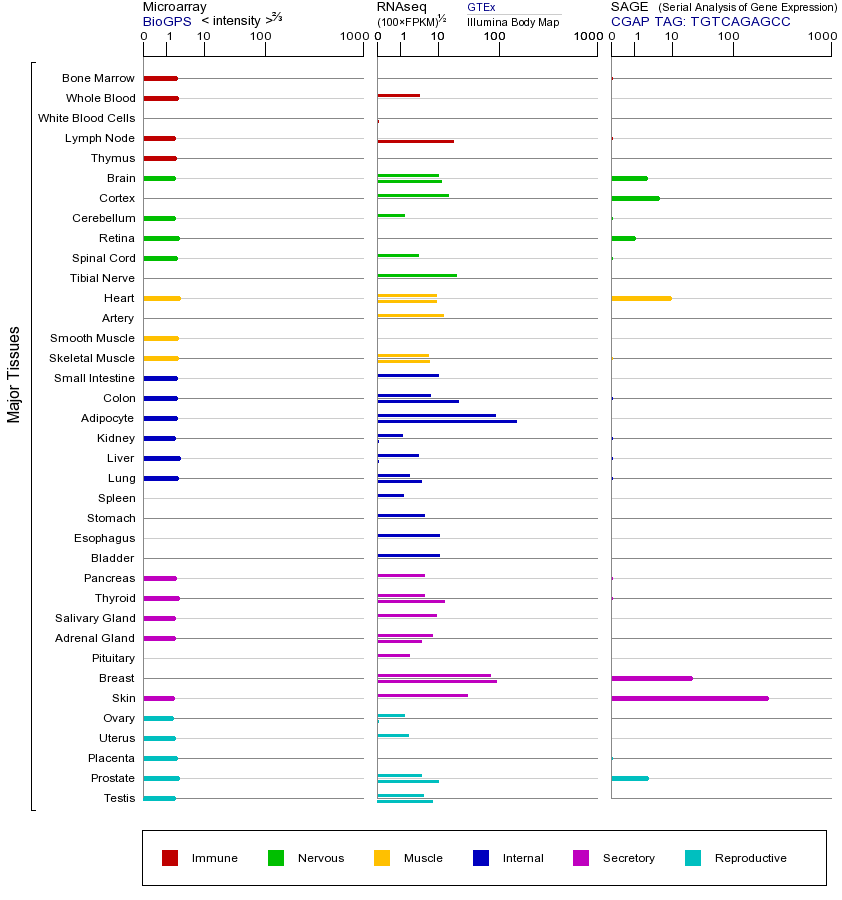
CIDEA(Cell Death-Inducing DFFA-Like Effector A)是一种在能量代谢和脂肪储存中起关键作用的基因,主要表达于脂肪组织、肝脏和免疫细胞中。它编码的蛋白质CIDEA通过调控脂滴的形成和融合来影响脂肪储存,尤其在白色脂肪组织中抑制脂肪分解,促进脂肪积累。CIDEA还参与线粒体功能调节,影响能量代谢和产热过程。该基因突变可能导致代谢紊乱,如肥胖、胰岛素抵抗和2型糖尿病。研究表明,CIDEA表达降低与脂肪分解增加和体重减轻相关,而过表达则促进脂肪积累和肥胖发展。此外,CIDEA在肿瘤细胞中也有表达,可能通过调节细胞凋亡和代谢影响肿瘤进展。CIDEA属于CIDEA基因家族,该家族包括CIDEA、CIDEB和CIDEC,这些成员在结构上具有相似性,均含有保守的死亡效应结构域(DED),并参与细胞死亡、代谢和免疫调节等过程。CIDEA家族基因在脂肪代谢和能量平衡中发挥重要作用,其异常表达与多种代谢性疾病和癌症相关。研究CIDEA及其家族基因为理解代谢调控和开发相关疾病治疗策略提供了重要线索。
This gene encodes the homolog of the mouse protein Cidea that has been shown to activate apoptosis. This activation of apoptosis is inhibited by the DNA fragmentation factor DFF45 but not by caspase inhibitors. Mice that lack functional Cidea have higher metabolic rates, higher lipolysis in brown adipose tissue and higher core body temperatures when subjected to cold. These mice are also resistant to diet-induced obesity and diabetes. This suggests that in mice this gene product plays a role in thermogenesis and lipolysis. Alternatively spliced transcripts have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]
这个基因编码已被证明以激活细胞凋亡的小鼠蛋白CIDEA的同源物。凋亡的这种激活是由DNA片段化因子DFF45但不受蛋白酶抑制剂抑制。当受到冷的小鼠缺乏功能CIDEA有较高的代谢率,棕色脂肪组织脂肪分解较高和更高的核心体温。这些小鼠也对饮食诱发的肥胖症和糖尿病性。这表明,在小鼠中这个基因产物起着热作用和脂肪分解作用。可变剪接转录物已经确定。 [由RefSeq的,2010年8月提供]
基因本体信息
CIDEA基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
CIDEA基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 疾病名称 | 关系值 | NofPmids | NofSnps | 来源 |
| Obesity | 0.124538567 | 9 | 1 | BeFree_CTD_human_GAD |
| Liver neoplasms | 0.12 | 1 | 0 | CTD_human |
| Metabolic Syndrome X | 0.003181358 | 3 | 1 | BeFree_GAD |
| Cachexia | 0.00272435 | 1 | 0 | LHGDN |
| Aortic Aneurysm, Abdominal | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
| Endometrial Carcinoma | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
| Vascular lesions | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
| Hyperinsulinism | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
| Aortic Aneurysm | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
| Dyslipidemias | 0.000271442 | 1 | 0 | BeFree |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。