EDDM3B (epididymal protein 3B)
- symbol:
- EDDM3B
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 14q11.2
- gene_family:
- alias symbol:
- HE3-BETA
- alias name:
- None
- entrez id:
- 64184
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000181552
- ucsc gene id:
- uc001vyd.3
- refseq accession:
- NM_022360
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:19223
- approved reserved:
- 2002-09-23
EDDM3B(Epidermal Differentiation Complex Member 3B)属于表皮分化复合体(Epidermal Differentiation Complex, EDC)基因家族,该家族位于人类染色体1q21上,包含多个与皮肤屏障形成和角质化过程相关的基因。EDC家族成员的共性在于它们编码的蛋白质大多参与表皮终末分化,维持皮肤屏障功能,并涉及角质形成细胞的增殖与凋亡平衡。EDDM3B的具体功能尚未完全阐明,但研究表明它可能在表皮分化中发挥作用,其表达产物可能参与细胞间连接或角质包膜的形成。该基因的突变或表达异常可能与皮肤疾病如银屑病、特应性皮炎或鱼鳞病相关,因这些疾病常伴随表皮分化障碍。若EDDM3B过表达,可能干扰正常角质形成程序,导致皮肤屏障缺陷或过度增殖;而表达降低则可能削弱表皮完整性,增加水分流失或外界刺激敏感性。目前研究提示EDDM3B与其他EDC成员(如FLG、LOR)存在功能协同,共同调控表皮稳态。由于EDC基因的紧密连锁,其表达常受共同调控元件影响,因此EDDM3B异常可能连带影响邻近基因功能。进一步研究需明确其精确分子机制及在疾病中的潜在治疗价值。
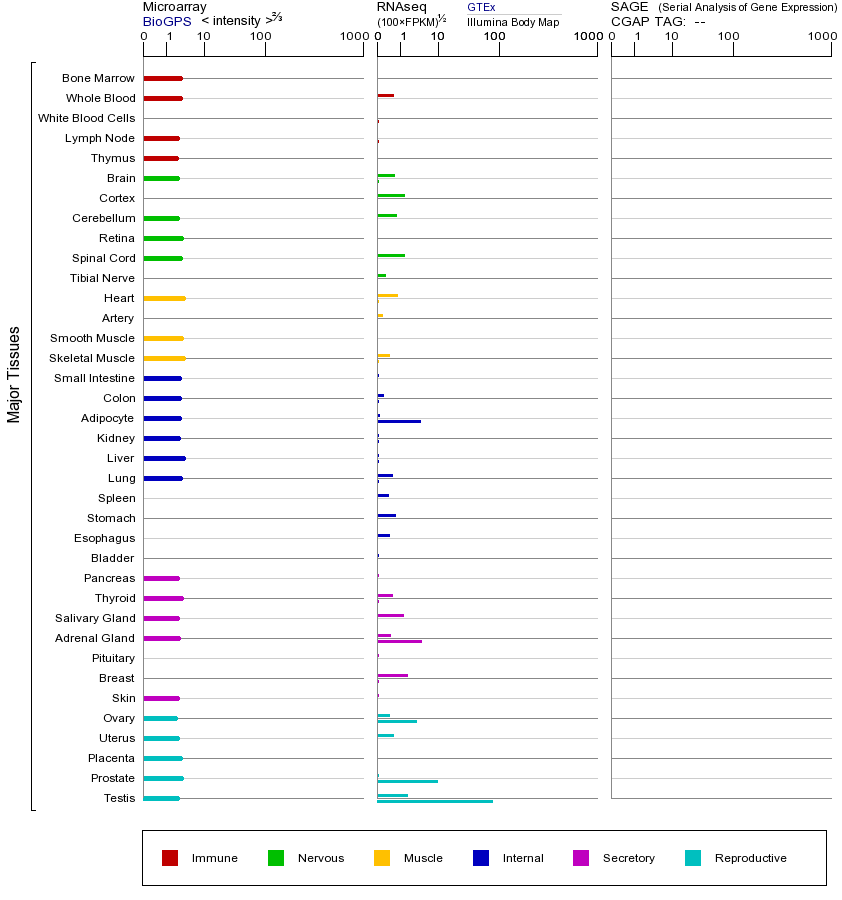
Testicular sperm are morphologically differentiated but are not progressively motile nor able to fertilize an egg. Post-testicular maturation requires exposure of spermatozoa to the microenvironment of the epididymal lumen. Spermatozoa undergo extensive changes in the epididymis, including enzymatic modifications, loss of pre-existing components and addition of new glycoproteins from epididymal secretions. These modifying proteins and enzymes are synthesized by epithelial cells lining the epididymal duct and secreted apically into the lumen, where they come into contact with, and may be absorbed onto, the sperm membranes. The proteins encoded by the genes in this cluster are synthesized and secreted by epididymal epithelial cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
睾丸精子形态上有区别,但不是逐步能动,也能够使卵子受精。睾丸后成熟需要精子暴露在附睾管腔的微环境。精子经过附睾丰富的变化,包括酶法修饰,预先存在的成分损失和增加的附睾分泌糖蛋白新。这些修饰的蛋白质和酶通过上皮细胞衬附睾管合成和顶部分泌入管腔,在那里它们与接触,并且可被吸收到,精子膜。通过在该簇的基因编码的蛋白质被合成,并通过附睾上皮细胞分泌。 [由RefSeq的,2008年7月提供]
基因本体信息
EDDM3B基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
EDDM3B基因的本体(GO)信息:
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。