NOTCH2 (notch receptor 2)
- symbol:
- NOTCH2
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 1p12
- gene_family:
- Ankyrin repeat domain containing
- alias symbol:
- None
- alias name:
- None
- entrez id:
- 4853
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000134250
- ucsc gene id:
- uc001eik.4
- refseq accession:
- NM_024408
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:7882
- approved reserved:
- 1994-11-10
NOTCH2属于NOTCH基因家族,该家族包括NOTCH1、NOTCH2、NOTCH3和NOTCH4四个成员,它们在进化上高度保守,主要参与细胞间通讯和信号传导,调控细胞分化、增殖和凋亡等关键生物学过程。NOTCH2编码的跨膜受体蛋白在NOTCH信号通路中起核心作用,通过与配体(如JAGGED或DELTA样蛋白)结合触发γ-分泌酶介导的蛋白水解,释放NOTCH2胞内结构域(NICD),后者转入细胞核调控靶基因表达。NOTCH2在胚胎发育中至关重要,尤其在肾脏、肝脏和骨骼系统的形成中发挥关键作用,还参与免疫细胞(如B细胞)的发育和功能调节。NOTCH2的功能异常与多种疾病相关,例如功能获得性突变导致Hajdu-Cheney综合征(表现为骨质疏松和颅面畸形),而功能缺失突变则与Alagille综合征(肝胆和心血管发育异常)相关。NOTCH2的过表达常见于某些癌症(如乳腺癌和胶质瘤),可能通过促进细胞增殖和抑制分化驱动肿瘤进展;相反,其表达降低可能影响组织稳态和再生能力。NOTCH基因家族的共性包括:均含有多个EGF样重复序列和LIN12/NOTCH结构域,通过保守的配体-受体相互作用激活下游信号,并依赖CSL(CBF1/RBP-Jκ)转录复合物调控效应基因。NOTCH2的活性受NUMB、DELEX等蛋白的负调控,其表达水平变化可能影响其他发育相关基因(如HES、HEY家族)的表达,形成复杂的调控网络。在癌症中,NOTCH2既可发挥促瘤或抑瘤作用,具体效应取决于细胞环境,例如在某些B细胞恶性肿瘤中表现出抑癌特性。对NOTCH2的深入研究有助于开发针对相关疾病的靶向疗法,如γ-分泌酶抑制剂或NOTCH2特异性抗体。
This gene encodes a member of the Notch family. Members of this Type 1 transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple, different domain types. Notch family members play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. The Notch signaling network is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway which regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signaling pathway that plays a key role in development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remain to be determined. This protein is cleaved in the trans-Golgi network, and presented on the cell surface as a heterodimer. This protein functions as a receptor for membrane bound ligands, and may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]
该基因编码所述Notch家族的一个成员。这种类型1的跨膜蛋白家族的成员共有的结构特征,包括由多个表皮生长因子样(EGF)的胞外域重复,和由多个不同的域类型的细胞内结构域。缺口家族成员通过控制细胞命运决定发挥各种发育过程中的作用。 Notch信号网络是其调节物理相邻细胞间的相互作用的进化上保守的细胞间信号传导途径。在Drosophilia,其细胞结合的配体(三角形,锯齿)缺口交互规定,起着发展的重要作用,细胞间信号通路。缺口配体的同系物也已在人确定,但这些配体与人Notch同源物之间的精确相互作用仍有待确定。这种蛋白质被裂解反式高尔基网络中,并呈现在细胞表面作为异二聚体上。该蛋白质的功能,作为膜结合配体的受体,和可能在血管,肾和肝发育的作用。编码不同亚型的两个转录变异体已被发现这个基因。 [由RefSeq的,2011年1月提供]
基因本体信息
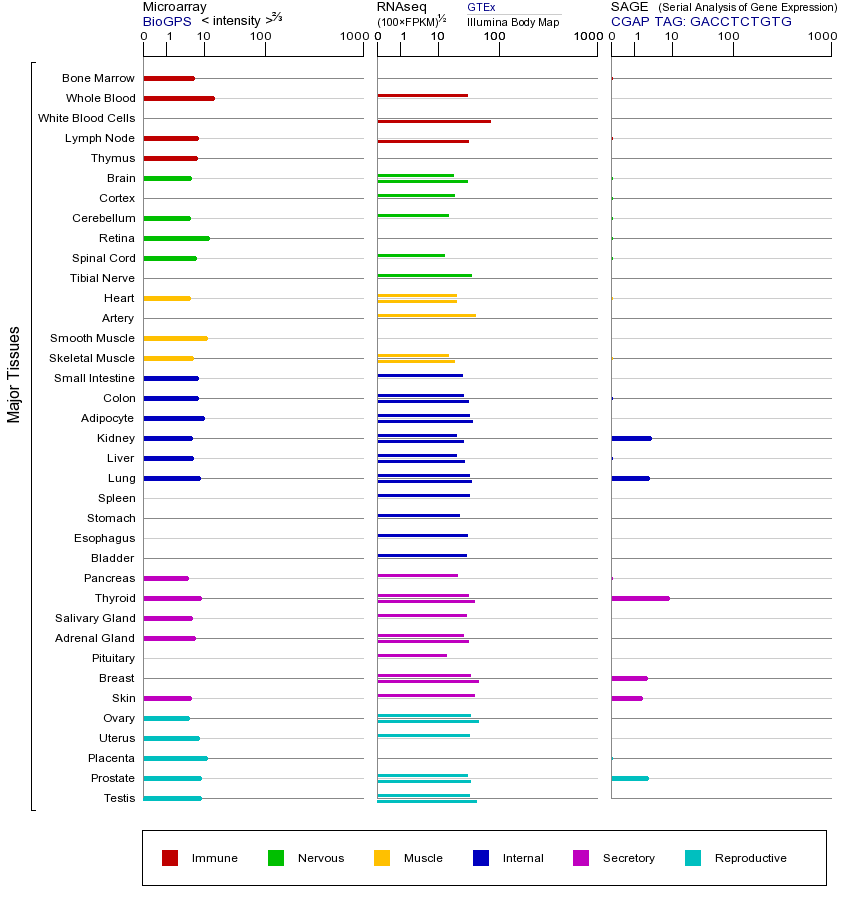
NOTCH2基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
NOTCH2基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 名称 |
|---|
| 4330 Notch signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04330] |
| 4919 Thyroid hormone signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04919] |
| 4320 Dorso-ventral axis formation [PATH:hsa04320] |
| 5206 MicroRNAs in cancer [PATH:hsa05206] |
| 名称 |
|---|
| A third proteolytic cleavage releases NICD |
| Gene Expression |
| Generic Transcription Pathway |
| NICD traffics to nucleus |
| Notch-HLH transcription pathway |
| NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus |
| NOTCH2 intracellular domain regulates transcription |
| Pre-NOTCH Expression and Processing |
| Pre-NOTCH Processing in Golgi |
| Pre-NOTCH Processing in the Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation |
| Receptor-ligand binding initiates the second proteolytic cleavage of Notch receptor |
| Signaling by NOTCH |
| Signaling by NOTCH2 |
| 疾病名称 | 关系值 | NofPmids | NofSnps | 来源 |
| Hajdu-Cheney Syndrome | 0.362985861 | 12 | 4 | BeFree_CLINVAR_CTD_human_ORPHANET |
| Alagille Syndrome 2 | 0.36 | 1 | 10 | CLINVAR_ORPHANET_UNIPROT |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent | 0.293160471 | 24 | 25 | BeFree_CTD_human_GAD_GWASCAT |
| Mammary Neoplasms | 0.128987376 | 6 | 1 | BeFree_CTD_human_LHGDN |
| Alagille Syndrome | 0.125167327 | 9 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human_LHGDN |
| Glioblastoma | 0.121085767 | 5 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human |
| Astrocytoma | 0.120271442 | 2 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human |
| Acroosteolysis dominant type | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | ORPHANET |
| Lung Neoplasms | 0.12 | 1 | 0 | CTD_human |
| Uterine Cervical Neoplasm | 0.12 | 1 | 0 | CTD_human |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。