PSMB11 (proteasome subunit beta 11)
- symbol:
- PSMB11
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 14q11.2
- gene_family:
- alias symbol:
- beta5t
- alias name:
- None
- entrez id:
- 122706
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000222028
- ucsc gene id:
- uc010ake.2
- refseq accession:
- NM_001099780
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:31963
- approved reserved:
- 2008-01-21
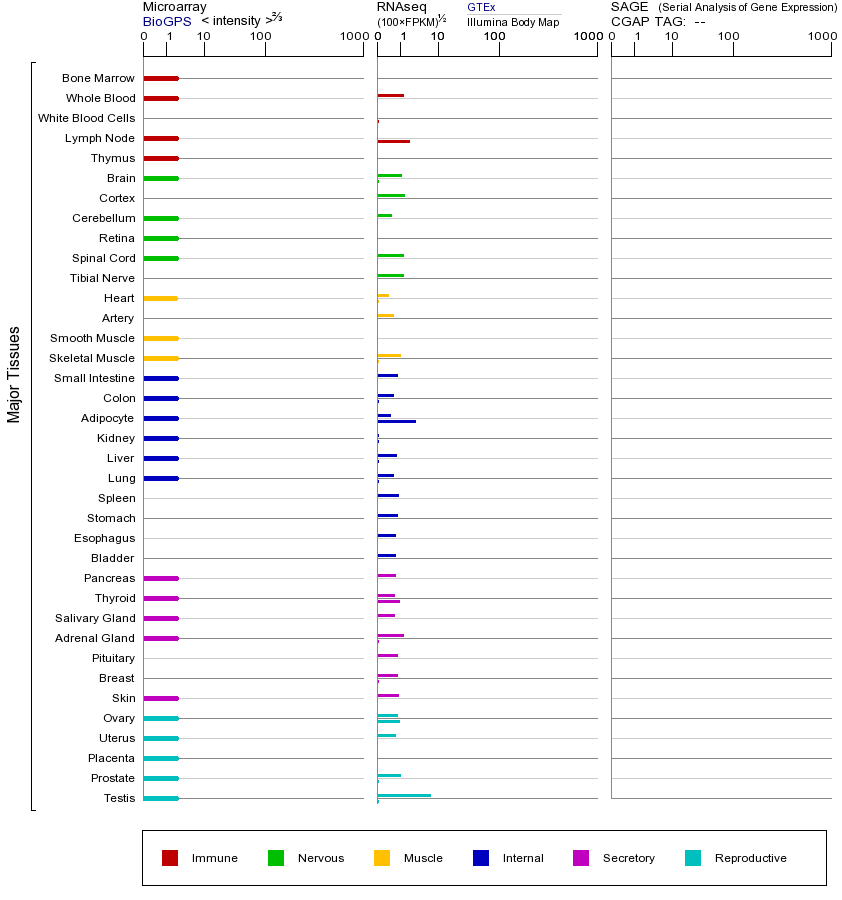
PSMB11(蛋白酶体亚基β型11)是蛋白酶体基因家族的一员,属于β亚型亚基,主要参与细胞内蛋白质的降解过程。蛋白酶体是一个大型多亚基复合物,负责通过泛素-蛋白酶体途径降解受损或错误折叠的蛋白质,从而维持细胞内蛋白质稳态。PSMB11主要在免疫系统中表达,特别是在胸腺上皮细胞中,可能参与胸腺细胞的选择和T细胞的发育。该基因的突变可能影响蛋白酶体的正常功能,导致蛋白质降解异常,进而可能引发免疫系统紊乱或自身免疫性疾病。过表达PSMB11可能增强蛋白质降解能力,但过度激活可能导致正常蛋白的过度降解,影响细胞功能;而降低表达则可能导致错误蛋白积累,引发细胞应激或凋亡。PSMB11属于蛋白酶体β亚基家族,该家族成员通常具有催化活性,负责切割蛋白质肽键。与其他家族成员相比,PSMB11可能在免疫特异性功能中发挥独特作用。研究表明,PSMB11可能与某些癌症或自身免疫疾病相关,但其具体机制仍需进一步研究。
Proteasomes generate peptides that are presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I molecules to other cells of the immune system. Proteolysis is conducted by 20S proteasomes, complexes of 28 subunits arranged as a cylinder in 4 heteroheptameric rings: alpha-1 to -7, beta-1 to -7, beta-1 to -7, and alpha-1 to -7. The catalytic subunits are beta-1 (PSMB6; MIM 600307), beta-2 (PSMB7; MIM 604030), and beta-5 (PSMB5; MIM 600306). Three additional subunits, beta-1i (PSMB9; MIM 177045), beta-2i (PSMB10; MIM 176847), and beta-5i (PSMB8; MIM 177046), are induced by gamma-interferon (IFNG; MIM 147570) and are preferentially incorporated into proteasomes to make immunoproteasomes. PSMB11, or beta-5t, is a catalytic subunit expressed exclusively in cortical thymic epithelial cells (Murata et al., 2007 [PubMed 17540904]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]
蛋白酶体产生由主要组织相容性复合体(MHC)I类分子的免疫系统的其它细胞呈递的肽。蛋白酶解由20S蛋白酶体进行的,布置在4 heteroheptameric环的圆筒28亚基络合物:α-1至-7,β-1至-7,β-1至-7,和α-1至-7。催化亚基β-1(PSMB6; MIM 600307),β-2(PSMB7; MIM 604030),和β-5(PSMB5; MIM 600306)。三个附加的亚基,β-1I(PSMB9; MIM 177045),β-2I(PSMB10; MIM 176847),和β-5I(PSMB8; MIM 177046),由γ-干扰素诱导的(IFNG; MIM 147570),并且优先纳入蛋白酶,使免疫蛋白酶。 PSMB11,或β-5T,是只在皮质胸腺上皮细胞中表达的催化亚基(Murata等人,2007年[搜索PubMed 17540904])。[由OMIM,2008年3月提供的]
基因本体信息
PSMB11基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
PSMB11基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 名称 |
|---|
| 3050 Proteasome [PATH:hsa03050] |
| 名称 |
|---|
| Activation of APC/C and APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins |
| Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells |
| Adaptive Immune System |
| Antigen processing-Cross presentation |
| Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation |
| APC:Cdc20 mediated degradation of cell cycle proteins prior to satisfation of the cell cycle checkpoint |
| APC/C-mediated degradation of cell cycle proteins |
| APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins |
| APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin |
| APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 |
| Apoptosis |
| Assembly of the pre-replicative complex |
| Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins |
| AUF1 (hnRNP D0) destabilizes mRNA |
| Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 |
| beta-catenin independent WNT signaling |
| C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) |
| Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A |
| CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 |
| CDT1 association with the CDC6:ORC:origin complex |
| Cell Cycle |
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic |
| Class I MHC mediated antigen processing & presentation |
| CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling |
| Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) |
| Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling |
| degradation of AXIN |
| Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex |
| degradation of DVL |
| Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome |
| Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome |
| Disease |
| Diseases of signal transduction |
| DNA Replication |
| DNA Replication Pre-Initiation |
| Downstream signaling events of B Cell Receptor (BCR) |
| ER-Phagosome pathway |
| G1/S DNA Damage Checkpoints |
| Gene Expression |
| GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome |
| Hedgehog 'off' state |
| Hedgehog 'on' state |
| Hedgehog ligand biogenesis |
| Hh mutants abrogate ligand secretion |
| Hh mutants that don't undergo autocatalytic processing are degraded by ERAD |
| HIV Infection |
| Host Interactions of HIV factors |
| Immune System |
| Infectious disease |
| Innate Immune System |
| M Phase |
| M/G1 Transition |
| Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives |
| Mitotic Anaphase |
| Mitotic Metaphase and Anaphase |
| Orc1 removal from chromatin |
| p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response |
| p53-Dependent G1/S DNA damage checkpoint |
| p53-Independent DNA Damage Response |
| p53-Independent G1/S DNA damage checkpoint |
| PCP/CE pathway |
| Programmed Cell Death |
| Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation |
| Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase |
| Regulation of Apoptosis |
| Regulation of DNA replication |
| Regulation of mitotic cell cycle |
| Regulation of mRNA stability by proteins that bind AU-rich elements |
| Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) |
| Removal of licensing factors from origins |
| S Phase |
| SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 |
| Separation of Sister Chromatids |
| Signaling by Hedgehog |
| Signaling by the B Cell Receptor (BCR) |
| Signaling by Wnt |
| Stabilization of p53 |
| Switching of origins to a post-replicative state |
| Synthesis of DNA |
| TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT |
| Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A |
| Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D |
| Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D1 |
| Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G |
| Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。